Biden and Zelensky sign security deal as Ukraine’s leader questions how long unity will last
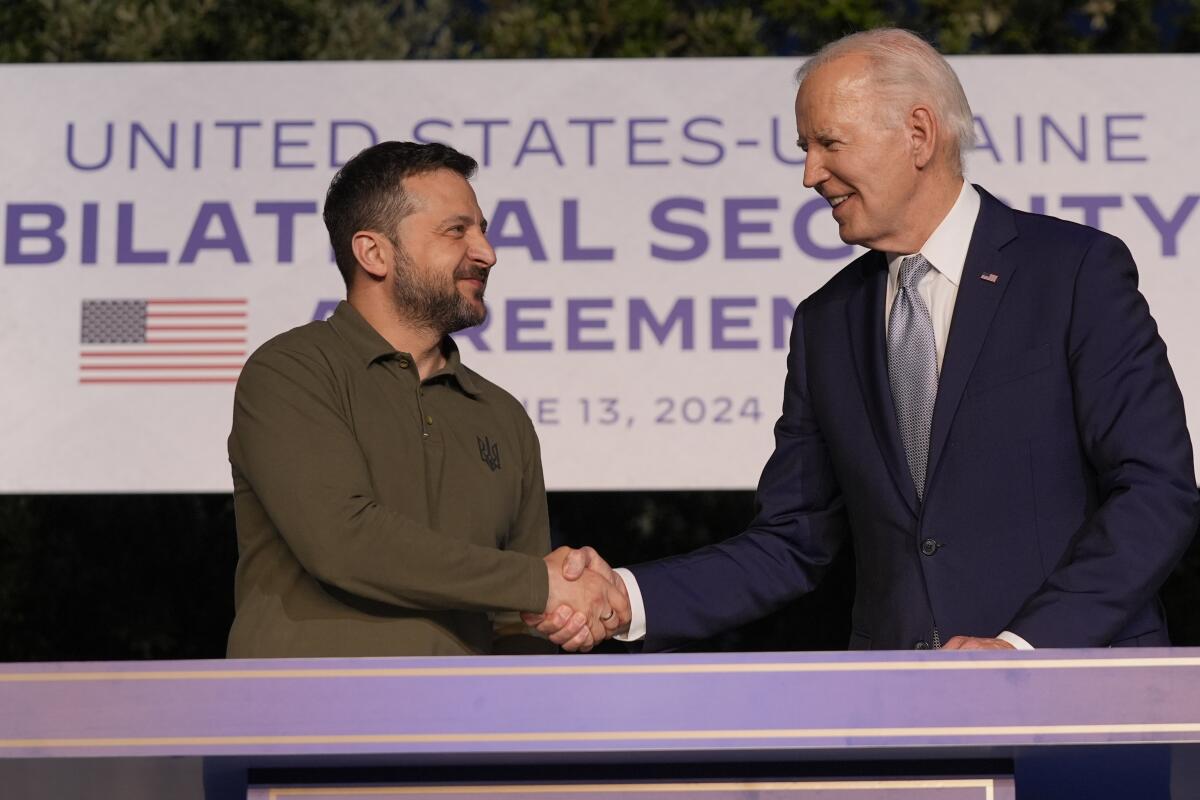

BORGO EGNAZIA, Italy — President Biden and Ukrainian leader Volodymyr Zelensky signed a 10-year security agreement Thursday that they hailed as a milestone in relations between their countries, but that alone was not enough to stop Zelensky from wondering how much longer he could count on America’s support.
Zelensky also said his country “urgently” needed additional air defense systems to protect Ukrainians and the nation’s infrastructure from Russia’s continued bombardment.
The leaders signed the agreement on the sidelines of the annual Group of 7 summit, held this year in Italy, and Biden said the goal “is to strengthen Ukraine’s defense and deterrence capabilities.”
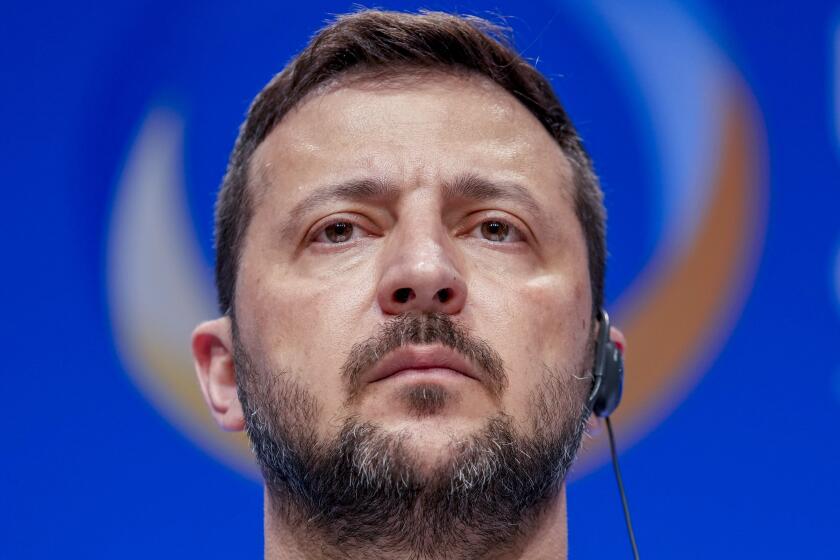
Zelensky said at a joint news conference that the signing made for a “truly historic day,” but he also wondered about the durability of support from the United States and other allies.
Ukraine’s president said the right question to ask is “for how long the unity in the world will remain? The unity in the U.S., together with European leaders” and how it will be influenced by the outcome of elections this year in many of those countries.
Ukrainian President Zelensky is all over Europe, including at the G-7. His message? Ukraine’s war with Russia and Putin is Europe’s fight, too.
Topping that list is voting in the U.S. in November in a campaign that could see the return of Republican Donald Trump to the presidency. Trump has been skeptical of providing additional military aid to Ukraine, at one point criticizing the “endless flow of American treasure.” He more recently has expressed openness to lending money instead and has said Ukraine’s independence is important to the United States.
Biden said the U.S. has commitments from five countries that he did not name to provide Patriot missile and other air defense systems to Ukraine. He said countries that have been expecting the same weapons from the U.S. have been told they will have to wait because “everything we have is going to go to Ukraine until their needs are met.”
European Parliament elections yield victory for centrists, but in France, far-right landslide triggers snap parliamentary elections.
Zelensky said he “urgently” needed seven Patriot systems. Biden then told him, “You’ll have some relatively quickly.”
Germany is one of the five countries that have promised an additional Patriot system for Ukraine.
Zelensky went on to deliver a stark warning about Russian aggression, saying that “if Ukraine does not withstand, the democracy of many countries, I am sure, won’t withstand either.”
The United States and European countries also agreed to lock up sanctioned Russian assets until Moscow pays reparations for its invasion of Ukraine, clearing the way for leaders to announce a $50-billion loan package for Ukraine. Combined with new sanctions against Russia announced earlier in the week, Biden said the series of actions to support Ukraine show Russian President Vladimir Putin that “he cannot wait us out. He cannot divide us.”
The highly anticipated agreement will leverage interest and income from the more than $260 billion in frozen Russian assets, largely held in Europe, to secure a $50-billion loan from the U.S. and additional loans from other partners. Ukraine will receive the first payments sometime this year, a U.S. official said. The official spoke on the condition of anonymity to preview the agreement, which will be included in the G-7 leaders’ communique on Friday.
Amid worsening Ukraine war outlook, an infusion of American military aid is seen as crucial in the fight against Russian invaders. Will it be enough?
Ukraine will be able to spend the money in several areas, including for military, economic and humanitarian needs and reconstruction, the official said.
The leaders’ statement will also leave the door open to confiscating the Russian assets entirely, for which the allies have yet to muster the political will, largely citing legal and financial stability concerns.
Biden and Zelensky met Thursday for the second time in two weeks to discuss the security agreement as the group of wealthy democracies has been looking for new ways to bolster Ukraine’s defenses against Russia.
The agreement on using frozen Russian assets to benefit Ukraine comes several months after the White House broke through a logjam in Congress that stalled approval of some $60 billion in U.S. aid for Ukraine. The delay gave Russia time to make gains on the battlefield. Biden publicly apologized to Zelensky for the holdup when they met last week in France.
Could Ukraine lose the war? Once nearly taboo, the question hovers in Kyiv, but Ukrainians believe they must fight for their lives against Putin’s troops.
The agreement does not commit U.S. troops directly to Ukraine’s defense against Russia. Biden does not want to have the U.S. pulled into a direct conflict with nuclear-armed Moscow.
The pact, which would remain in effect for 10 years, does not offer Ukraine any new money but includes a commitment by the U.S. to work with Congress on a source of sustainable funding for the future. Text of the agreement released by the White House also describes how the U.S. will coordinate with Ukraine and other U.S. allies and partners to make sure Ukraine has the military, intelligence and other means necessary to defend itself and deter Russian aggression.
The U.S. and Ukraine would also consult “at the highest levels” in the event of a future armed attack by Russia against Ukraine. Either side can terminate the agreement in writing with six months’ notice, which means a future U.S. president, including Trump if elected in November, could cancel the arrangement.
Scores of countries and organizations are set to meet over the weekend in Switzerland to discuss peace for Ukraine. Biden is not scheduled to attend the summit, and that has disappointed Zelensky. Vice President Kamala Harris will represent the U.S. instead while the Democratic president attends a campaign fundraiser in Los Angeles.
Touring Europe for the first time in five years, Chinese President Xi has sought to both woo and divide. Ukraine and trade are wedge issues for China.
It wasn’t just Ukraine that occupied the allies’ attention.
Biden announced that Italy was joining a G7 initiative to provide development assistance to Africa, which is meant as a bulwark against growing Chinese influence on the continent. Biden said $60 billion mobilized by the U.S. and the G7 is proof “democracies can deliver,” as the U.S. and its allies warn that China’s investments come attached with geopolitical and economic demands.
The G-7 summit opened Thursday in Italy’s picturesque Puglia region in the south with leaders meeting in private as they discussed the war in Gaza, support for Ukraine and other mutual concerns.
The group of industrialized democracies — the U.S., Britain, Canada, France, German, Italy and Japan, plus European governing bodies — meets annually. Italy holds the rotating presidency this year, and far-right Prime Minister Giorgia Meloni is hosting.
The trip is Biden’s second outside the U.S. in as many weeks; he was in France last week for a state visit and ceremonies commemorating the 80th anniversary of the D-day landings in World War II.
Long and Superville write for the Associated Press. Superville reported from Fasano, Italy.
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.