A majority of Black Americans believe U.S. institutions are conspiring against them, a Pew poll finds

WASHINGTON — Most Black Americans say they’ve experienced racial discrimination regularly or from time to time, which colors how they view U.S. institutions like policing, the political system and the media, according to a study on conspiracy theories.
The study released Monday by the Pew Research Center examined the intersection of race and conspiratorial beliefs. It’s the second installment in the research group’s series on how Black Americans see success and failure.
The study defines racial conspiracy theories as ideas that Black Americans might have about “the actions of U.S. institutions” that aren’t necessarily the stated goals of the institution. The study stresses that these are claims that Black Americans may have because of America’s documented history of racist policies largely affecting Black communities. Pew examined claims including conspiratorial beliefs about how major institutions discriminate against Black Americans and support for generational adages such as “you have to work twice as hard” to advance compared with white Americans.
‘I’m not captive any more,’ says a Californian now living in Costa Rica — one of many Black Americans citing racism as why they’re leaving the U.S.
For instance, the study found that more than 8 in 10 Black Americans surveyed agreed with the statement that “Black people are more likely to be incarcerated because prisons want to make money on the backs of Black people.” And more than 6 in 10 Black adults surveyed agreed that institutions such as the criminal justice system, the country’s economic system and policing are designed to hold Black people back.
Those sentiments exist alongside a reality that Black people were 32% of sentenced state and federal prisoners in 2022, even though they make up just 12% of the overall U.S. population. By comparison, white people were underrepresented among prisoners at 31%, while Hispanic people were slightly overrepresented at 23% of prisoners, according to the Bureau of Justice Statistics.
Pew’s study draws from a poll of Black Americans conducted in September. Study authors say that views are unlikely to have shifted since the respondents were surveyed.
Jamaica native Winsome Pendergrass is part of a surge of immigrants from Africa and the Caribbean. She supports solidarity among Black Americans, but has been shunned in return.
The study also explored why Black adults believe these narratives and allowed respondents to explain how they feel about discrimination and racial disparities in their own words, said senior Pew researcher and study author Kiana Cox.
She added that although the survey was released during an election year it does not focus on partisan politics. Rather, it showcases the feelings Black Americans have that can influence how the community views the nation but often go unheard or aren’t taken seriously.
“There are anecdotal conversations among Black people about the system, the Man, the invisible hand, the agenda that is set out to create a situation where Black people can’t advance. So, we wanted to explore that,” Cox said. “We also wanted to figure out how many Black people are familiar with these narratives about the system being designed for their failure and how many Black people believe them.”
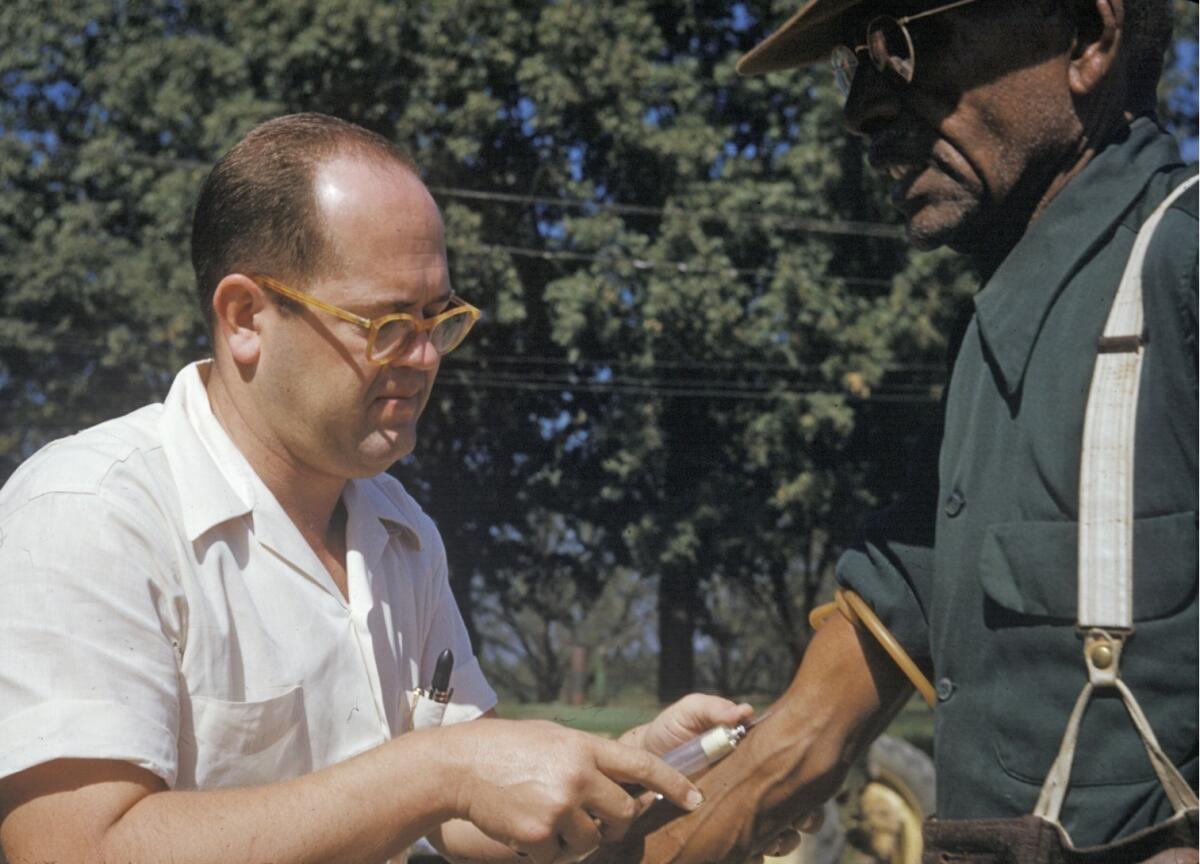
It’s not just the infamous Tuskegee syphilis study, Black Americans’ skepticism about COVID vaccines is fueled by health inequities they face now.
Americans are far from impervious to conspiratorial thinking dating to the founding of the nation, a legacy that has gained new life as the internet supercharged communication and, often, the spread of misinformation and hoaxes. The Pew study notes that Black Americans have a unique relationship with both discrimination and claims of government conspiracy theories given the nation’s legacy of slavery, Jim Crow-era segregation laws and modern-day discrimination against Black Americans by public and private actors.
“When you have a history of American institutions actually conspiring against Black people, it’s not so hard to believe that anything else would also be true,” said Tasha Philpot, a professor of political science at the University of Texas at Austin, who studies political psychology among Black Americans.
“Especially in the last few years where race has been pretty salient, it doesn’t surprise me that people would say they are experiencing racial discrimination,” she said.
Among Black adults who have experienced discrimination, about three-quarters said it made them feel as though the system as a whole was designed to keep them down. Black adults who have faced discrimination also felt varying emotions as a result — 76% felt angry overall, 53% said they worried about their personal safety, and 41% felt depressed, for example. Researchers surveyed 4,736 Black, multiracial Black and non-Hispanic, and Black and Hispanic respondents in September from across the country.
The higher mortality rate among Black Americans resulted in 1.63 million excess deaths relative to white Americans over more than two decades, a study finds.
Black Americans were also likely to believe racial conspiracy theories about politics. Three-quarters of those surveyed said they agreed that “Black public officials being singled out to be discredited more than white officials” happens in politics today. In medicine, the study found that 55% of those surveyed said they agreed with the statement that “medical researchers experiment on Black people without their knowledge or consent.”
Philpot said some Black Americans may still believe such theories, given documented episodes of discrimination such as the Tuskegee syphilis experiment and the exclusion of Black Americans from New Deal programs that benefited white Americans.
“It’s not really a conspiracy theory if it’s true,” she said.
Alexander and Brown write for the Associated Press.
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.