Michigan, Vermont join California in enshrining abortion rights in state constitution

WASHINGTON — Voters in battleground Michigan enshrined abortion rights in the state constitution Tuesday, joining reliably Democratic California and Vermont in taking that step, while a measure in Kentucky to amend the constitution to say there is no right to abortion failed.
The Kentucky result bucked the state’s Republican-led Legislature, which had imposed a near-total ban on the procedure and put the proposed state constitutional amendment on the ballot. It also mirrored what happened in another red state, Kansas, where voters in August rejected changing that state’s constitution to let lawmakers tighten restrictions or ban abortions.
The ballot measures came months after the Supreme Court overturned Roe vs. Wade and the constitutional right to abortion nationwide. The decision in June has led to near-total bans in a dozen states.
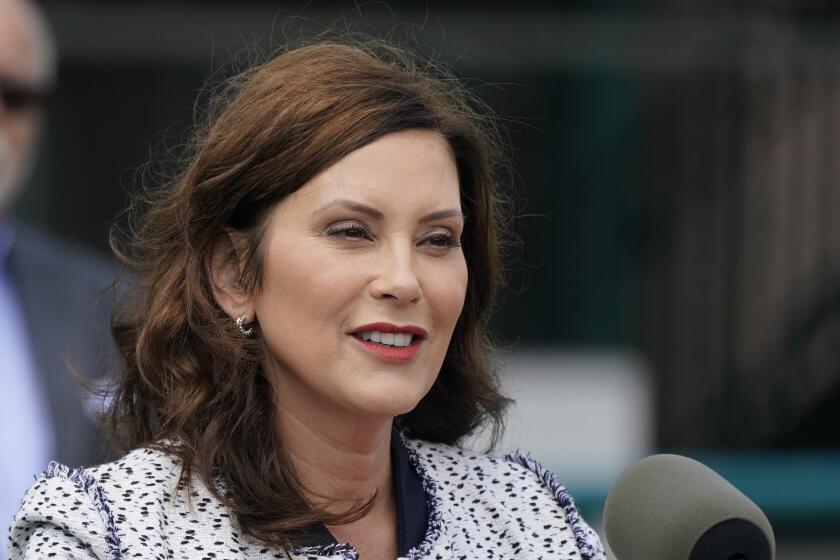
Supporters of the push to protect abortion rights in Michigan collected more signatures than any other ballot initiative in state history to get it before the voters. It puts a definitive end to a 1931 ban on abortion that had been blocked in court but could have been revived. It also affirms the right to make pregnancy-related decisions about abortion and other reproductive services such as birth control without interference.
On Michigan State University’s campus, junior Devin Roberts said that students seemed “fired up” and that he had seen lines of voters spilling out of the school’s polling places throughout the day. The ballot measure was one of the main drivers of the high turnout, he said.
“There’s a lot of energy for [Proposition] 3 on campus right now, whether you agree with abortion or not,” Roberts said. “I think students want to have the same rights that their parents had when they were younger.”
Whitmer led a statewide ticket of Democrats that centered their campaigns on abortion rights after the U.S. Supreme Court’s overturning of Roe vs. Wade.
Nationally, about two-thirds of voters say abortion should be legal in most or all cases, according to AP VoteCast, an expansive survey of more than 90,000 voters across the country. Only about 1 in 10 say abortion should be illegal in all cases.
About 6 in 10 also say the Supreme Court’s abortion decision made them dissatisfied or angry, compared with fewer who say they were happy or satisfied.
James Miller, 66, of Flint, Mich., said he thought of his daughters, granddaughters and great-granddaughters when he voted in favor of the measure.
“I think we should do the right thing for women,” he said. “It’s her body; it’s her privacy.”
The logistics of accessing abortion are about to get more complicated, with at least 26 states set to ban the procedure after the fall of Roe vs. Wade.
Michelle Groesser of Swartz Creek, Mich., said she opposed abortion, even though she believes that any ban likely would have some narrow exceptions. “In a perfect world, I personally would want all life preserved,” she said.
Opponents have contended that the Michigan measure could have far-reaching effects on other laws in the state, such as one requiring parental notification of an abortion for someone under 18. Legal experts say changes to other laws would happen only if someone sued and won, a process that could take years and would have no certainty of success.
Even so, the messaging appeared to resonate with some Michigan voters, including Brian Bauer, 64, of Mundy Township, who said the proposal was confusing and voted against it.
Bauer is an abortion opponent who supports some limited exceptions, “but nobody’s willing to throw [in] any kind of compromise. ... It’s either a yes or no vote.”
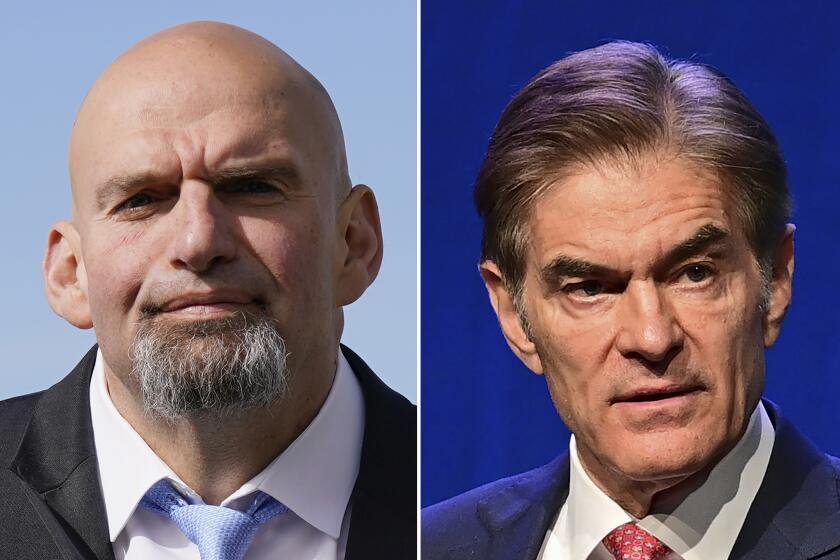
John Fetterman, who campaigned after suffering a stroke, defeats Trump-endorsed Mehmet Oz in a Senate race marked by attacks and trolling.
Montana voters, meanwhile, were also considering newborn resuscitative care requirements with possible criminal penalties, including the rare case of an attempted abortion.
In Kentucky, lawmakers added the proposed constitutional amendment to the ballot last year, a move that some thought would drive more conservative voters to the polls. But after the Supreme Court decision in June, abortion rights supporters raised nearly $1.5 million to fight it.
Initial returns indicated that thousands of Kentucky voters who backed GOP Sen. Rand Paul for reelection opposed the abortion amendment.
At an elementary school in Simpsonville, a small town outside of Louisville, 71-year-old Jim Stewart said he voted for Paul, calling him “the only one on TV making sense.”
Stewart is a registered Republican and opposed to abortion, but still voted no on the amendment. “You got to have a little choice there.”
Al Smith, 83, voted yes. “I don’t believe in abortion at all, not for any circumstance,” he said.
The ballot question in Vermont came after the Legislature passed a law in 2019 guaranteeing reproductive rights, including getting pregnant and having access to birth control. Supporters from the Reproductive Liberty Ballot Committee said the overturning of Roe vs. Wade meant “state-level protections are vital to safeguarding access to reproductive health care.”
California already had passed several measures aimed at easing access to abortion and set aside millions of taxpayer dollars to help pay for some out-of-state abortion travel. On Tuesday, voters approved language to be added to the state constitution that would explicitly guarantee access to abortion and contraception.
In Montana, voters faced a question on whether to create criminal penalties for healthcare providers unless they do everything “medically appropriate and reasonable” to save the life of a baby after birth, including the rare possibility of birth after an attempted abortion.
More to Read
Get the L.A. Times Politics newsletter
Deeply reported insights into legislation, politics and policy from Sacramento, Washington and beyond. In your inbox three times per week.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.